Maintaining a properly functioning suspension system is crucial for ensuring a smooth and safe ride in any vehicle. Among the various maintenance tasks involved, greasing the suspension stands out as a vital step in prolonging the lifespan of your suspension components and optimizing their performance. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of suspension maintenance and provide you with a step-by-step walkthrough on how to grease your suspension effectively.
As we explore the intricacies of greasing suspension, we will begin by familiarizing ourselves with the different components that make up a suspension system and understanding their roles in providing a comfortable and stable ride. We will then delve into the types of suspension systems commonly found in vehicles today, examining the specific considerations for greasing each type.
Understanding Suspension Components
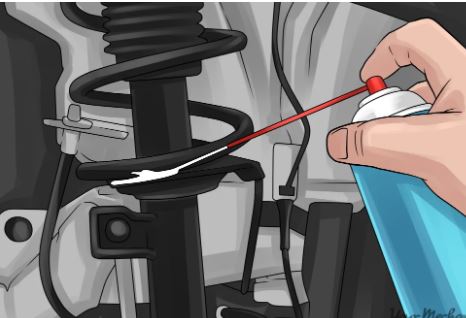
A vehicle’s suspension system consists of several key components that work together to provide a smooth and controlled ride. Understanding these components is crucial for proper maintenance and greasing of the suspension system. Let’s take a closer look at each of these components:
- Springs: Springs are responsible for supporting the weight of the vehicle and absorbing shocks from the road. They come in various types, such as coil springs and leaf springs, depending on the vehicle’s design. Springs help maintain the vehicle’s ride height and contribute to overall stability.
- Shock Absorbers: Shock absorbers, also known as dampers, are crucial for controlling the up-and-down movement of the suspension. They work in conjunction with springs to absorb shocks and vibrations from uneven road surfaces. Shock absorbers play a vital role in maintaining tire contact with the road, enhancing stability, and providing a comfortable ride.
- Control Arms: Control arms, also called A-arms or wishbones, connect the suspension components to the vehicle’s chassis. They act as a link between the wheels and the frame, allowing for up-and-down movement while maintaining proper alignment. Control arms come in various shapes and sizes, depending on the suspension system’s design.
- Ball Joints: Ball joints are pivot points that connect the control arms to the steering knuckles. They allow for smooth movement and rotation of the front wheels while maintaining stability. Properly functioning ball joints are crucial for steering responsiveness and overall handling.
- Bushings: Bushings are rubber or polyurethane components that provide cushioning and allow for smooth movement between various suspension parts. They reduce noise, vibrations, and harshness (NVH) and help absorb road irregularities. Bushings are commonly found in control arms, sway bars, and other suspension components.
- Sway Bars: Sway bars, also known as stabilizer bars or anti-roll bars, are designed to reduce body roll during cornering. They connect the left and right sides of the suspension, helping distribute the weight evenly and improving stability. Sway bars play a vital role in enhancing handling and control.
- Struts: Struts are a common suspension component found in many vehicles, particularly in the front suspension. They combine the functions of a shock absorber and a coil spring into a single unit. Struts provide structural support, dampen vibrations, and contribute to the overall stability and handling of the vehicle.
Types of Suspension Systems
1. Independent Suspension
Independent suspension systems are designed to allow each wheel to move independently of the others. This type of suspension provides a smoother ride and better handling by absorbing shocks and bumps individually. Examples of independent suspension systems include MacPherson strut and double wishbone suspension.
- MacPherson Strut: This type of suspension system combines the shock absorber and coil spring into a single unit, simplifying the design and reducing weight. It is commonly found in many front-wheel-drive vehicles.
- Double Wishbone Suspension: The double wishbone suspension uses two control arms to connect the wheel hub to the chassis. It offers excellent handling characteristics and is often found in high-performance and luxury vehicles.
2. Dependent Suspension
Dependent suspension systems, also known as solid axle suspension, connect both wheels on an axle together. These systems provide greater stability but sacrifice some ride comfort and handling compared to independent suspension.
- Leaf Spring Suspension: Leaf springs consist of several layers of metal strips or leaves that are attached to the axle and vehicle frame. This suspension type is commonly found in trucks and heavy-duty vehicles due to its durability and load-carrying capacity.
- Live Axle Suspension: Live axle suspension systems utilize a solid beam axle that connects the wheels on each side of the vehicle. This type of suspension is often found in rear-wheel-drive trucks and SUVs.
3. Air Suspension
Air suspension systems use compressed air to support the weight of the vehicle and provide a smooth and adjustable ride. These systems allow for varying ride heights, improved handling, and enhanced comfort.
- Air Bag Suspension: Airbags replace traditional coil or leaf springs and can be inflated or deflated to adjust the ride height and stiffness of the suspension. This type of suspension is commonly found in luxury vehicles and high-end SUVs.
- Self-Leveling Suspension: Self-leveling suspension systems utilize air springs and sensors to automatically adjust the suspension height based on load conditions. This ensures a consistent ride height and improved handling regardless of the vehicle’s load.
Choosing the Right Grease
When it comes to greasing your suspension, selecting the appropriate grease is crucial for the optimal performance and longevity of your components. Here are some key factors to consider when choosing the right grease for your suspension system:
- Suspension Component Compatibility: Different suspension components may have specific grease requirements. It is essential to consult your vehicle’s manufacturer guidelines or service manual to determine the recommended grease types for each component. For example, some components may require a high-temperature grease, while others may need a specialized grease for specific conditions.
- Operating Conditions: Consider the typical operating conditions your vehicle encounters. Factors such as temperature extremes, moisture levels, and exposure to dust or dirt can influence the choice of grease. For example, if you frequently drive in extreme heat or cold, you may need a grease with superior temperature resistance. Similarly, if you often drive off-road or in muddy environments, a grease with excellent water resistance and anti-corrosion properties would be ideal.
- Grease Consistency and NLGI Rating: Grease consistency refers to its thickness and stiffness. It is typically categorized by the National Lubricating Grease Institute (NLGI) rating, ranging from 000 (semi-fluid) to 6 (hard). The NLGI rating indicates the grease’s ability to stay in place and provide lubrication under various conditions. For most suspension applications, a grease with an NLGI rating of 1 or 2 is commonly recommended.
- Additives and Performance Enhancers: Some greases are formulated with additives to enhance specific properties. For suspension greases, additives such as anti-wear agents, extreme pressure (EP) additives, corrosion inhibitors, and oxidation resistance additives can provide additional protection and improve performance. Consider the specific needs of your suspension system and explore greases that offer suitable additives for those requirements.
- Compatibility with Other Lubricants: In certain cases, you may have multiple lubricants in your suspension system, such as different types of greases or oils. It is essential to ensure that the grease you choose is compatible with any existing lubricants to prevent any adverse chemical reactions or performance issues. Consult the product labels, manufacturer recommendations, or seek professional advice to determine compatibility.
- Quality and Brand Reputation: Selecting a reputable brand and high-quality grease can significantly impact the overall performance and durability of your suspension components. Look for greases from trusted manufacturers known for their commitment to quality and adherence to industry standards. Reading customer reviews and seeking recommendations from automotive experts can help you make an informed decision.
Tools and Equipment Required
Before you begin greasing your suspension, gather the following tools and equipment to ensure a smooth and efficient process:
- Grease Gun: A high-quality grease gun is essential for applying grease to your suspension components. Opt for a gun with a comfortable grip and a flexible hose for reaching tight spots.
- Grease: Choose a high-performance grease specifically designed for automotive suspension systems. Look for a grease that offers excellent lubrication properties and is compatible with the materials used in your suspension components.
- Socket Set: A socket set with a variety of socket sizes will be needed to remove and reinstall components during the greasing process. Ensure that you have both metric and standard socket sizes to accommodate different suspension systems.
- Wrenches: Have a set of open-end or adjustable wrenches on hand to assist with loosening and tightening nuts and bolts. Wrenches with ratcheting mechanisms can make the task easier and more efficient.
- Torque Wrench: A torque wrench is necessary for accurately tightening fasteners to the manufacturer’s recommended specifications. This helps prevent over-tightening or under-tightening, ensuring proper assembly and performance.
- Safety Equipment: Prioritize your safety by wearing protective gear such as safety goggles, gloves, and work boots. These will shield you from potential hazards and prevent injuries during the greasing process.
- Cleaning Supplies: Prepare a supply of rags, shop towels, or disposable wipes to clean the suspension components and wipe away any excess grease. Also, have a suitable degreaser or brake cleaner to remove stubborn grime and old grease.
- Jack and Jack Stands: A reliable hydraulic jack and sturdy jack stands are necessary for lifting and securing your vehicle safely. Always follow proper lifting procedures and choose appropriate locations for jacking up your vehicle.
- Penetrating Lubricant: It is helpful to have a penetrating lubricant like WD-40 or PB Blaster to loosen rusted or seized components. Apply the lubricant and allow it to penetrate before attempting to remove stubborn parts.
- Shop Light: Adequate lighting is crucial for a thorough inspection of your suspension components. A portable shop light or a reliable flashlight will help you identify any issues or potential areas that require greasing.
- Disposable Gloves: Disposable gloves keep your hands clean and protect you from grease, grime, and potential chemical exposure. Choose gloves that offer good dexterity, so you can handle tools and components easily.
- Shop Creeper or Mat: If you have a shop creeper or a comfortable mat, it can provide a more comfortable working environment when accessing hard-to-reach areas under the vehicle. It also helps protect your back and knees.
Step-by-Step How to Grease Suspension
To ensure optimal performance and longevity of your suspension, follow this step-by-step greasing procedure for both the front and rear suspensions:
A. Front Suspension
- Step 1: Removing dust caps or covers
Locate the dust caps or covers on the front suspension components.
Use a suitable tool, such as a flathead screwdriver, to gently pry off the dust caps or covers.
Set the caps or covers aside in a safe place to avoid misplacement.
- Step 2: Applying grease to specific points
Refer to the manufacturer’s documentation or service manual to identify the grease points on the front suspension.
Attach a grease gun with the appropriate nozzle or attachment to the grease fitting on each designated point.
Slowly and evenly apply the recommended amount of grease, ensuring it flows smoothly into the joint or bushing.
If the grease begins to overflow or becomes excessively difficult to inject, stop greasing and seek professional assistance.
- Step 3: Reinstalling dust caps or covers
Once you have greased all the designated points, clean any excess grease around the fittings.
Align the dust caps or covers with their respective openings on the suspension components.
Gently press or tap the caps or covers into place until they are securely seated.
B. Rear Suspension
- Step 1: Accessing the rear suspension points
Depending on your vehicle’s design, the rear suspension points may require different access methods.
Use appropriate tools to remove any necessary components (such as wheel arch liners or trim panels) to gain access to the rear suspension points.
Exercise caution and refer to the vehicle’s service manual to ensure you are removing the correct components.
- Step 2: Applying grease to specific points
Similar to the front suspension, consult the manufacturer’s documentation or service manual to identify the specific greasing points for the rear suspension.
Attach the grease gun with the appropriate nozzle or attachment to the grease fitting on each designated point.
Slowly and evenly inject the recommended amount of grease into each point, ensuring it spreads effectively throughout the joint or bushing.
As with the front suspension, be mindful of excess grease and seek professional assistance if necessary.
- Step 3: Securing the suspension components
After greasing all the rear suspension points, ensure that any components you removed for access are securely reinstalled.
Double-check that all fasteners, such as bolts or clips, are properly tightened according to the manufacturer’s specifications.
Conduct a visual inspection to verify that all connections and components are in their correct positions.
FAQ About How to Grease Suspension
What is the recommended frequency for greasing suspension?
The recommended frequency for greasing suspension can vary depending on several factors, including the vehicle’s make and model, driving conditions, and the type of suspension system. As a general guideline, it is recommended to grease your suspension components every 12,000 to 15,000 miles or annually. However, it’s important to consult your vehicle’s service manual or manufacturer for the specific greasing interval.
Can I use any type of grease for my suspension components?
No, it is not recommended to use just any type of grease for your suspension components. Suspension systems require a specialized grease that is specifically designed for high-pressure applications, withstands extreme temperatures, and provides the necessary lubrication properties. It is important to use a grease that meets the manufacturer’s specifications and is suitable for the particular suspension components you are greasing.
How do I know if my suspension needs greasing?
There are several signs that indicate your suspension may need greasing:
Increased noise or squeaking from the suspension components
Reduced suspension performance, such as a harsh or bumpy ride
Excessive vibration or bouncing while driving
Irregular tire wear or uneven ride height
Difficulty steering or a loose, imprecise feel in the steering wheel
If you notice any of these symptoms, it is advisable to have your suspension inspected and greased if necessary.
Can I grease my suspension myself, or should I consult a professional?
Greasing your suspension can be done yourself if you have the necessary tools, knowledge, and access to the manufacturer’s guidelines. However, it is essential to ensure that you are comfortable and confident in performing the task correctly. If you are unsure or lack experience, it is recommended to consult a professional mechanic or technician who specializes in suspension maintenance. They have the expertise and equipment to perform the greasing accurately and safely.
Is greasing the suspension a difficult task?
Greasing the suspension can vary in difficulty depending on your familiarity with the vehicle and the specific suspension components. It generally involves accessing the grease points, using a grease gun, and applying the appropriate amount of grease to each designated area. While the procedure itself may not be overly complex, it requires attention to detail and adherence to proper greasing techniques. If you are unfamiliar with the process or lack experience, it is advisable to seek professional assistance.
What are the potential risks of inadequate greasing?
Inadequate greasing of suspension components can lead to various issues, including:
Increased friction and wear on suspension parts, leading to premature failure.
Reduced suspension performance and compromised ride quality.
Suspension noise and squeaking.
Uneven tire wear, affecting vehicle handling and stability.
Safety risks, as insufficiently lubricated components may result in unpredictable behavior while driving.
Regular greasing helps mitigate these risks by ensuring proper lubrication and reducing the chances of component failure.
Final Thought
In the end, regular greasing of your suspension system is a vital aspect of vehicle maintenance that should not be overlooked. Greasing your suspension components ensures optimal performance, extends their lifespan, and contributes to a smoother and safer driving experience.
Throughout this comprehensive guide, we have covered various aspects of greasing suspension, including understanding suspension components, selecting the right grease, preparing for greasing, step-by-step greasing procedures for front and rear suspension, special considerations for off-road vehicles, maintenance schedules, signs of greasing issues, troubleshooting, and the potential risks of inadequate greasing.
Related Topic:
- When to Use White Lithium Grease on Rubber Bushings
- How To Remove Grease From Hands And Nails
- Where to Put Dielectric Grease on Spark Plugs
- What Happens If You Don’t Grease Brake Pads
- Different Types of Grease
- Can You Use Dielectric Grease on Brake Caliper Pins
- White Lithium Grease vs WD-40
- Is Red and Tacky Grease Good for Wheel Bearings
- what happens if you don’t grease your ball joints


